SEO Guides, Tips & More!
Learn from Our Experience
How to Adapt to AI’s Search Takeover
AI is here to stay. A recent study by TrustRadius further cemented this conclusion. With 90% of B2B buyers clicking on AI overview citations, its clear where search is headed—towards AI. To fully comprehend and prepare for the impact of this AI-fueled disruption, it’s important to look at the currently available AI tools used for search and how they impact search.
In Summary
- The AI Shift Inside Google: Google’s AI Overviews (AIOs) and the new ‘AI Mode’ are steering search toward providing direct answers on the results page, often leading to “zero-click” searches. This fundamental change is undermining the traditional ad-supported financial model of content creation by reducing traffic to external websites.
- The AI Shift Outside Google: External large language model (LLM) chatbots like ChatGPT and Perplexity are attracting certain search activity with their conversational interface and generated answers. This trend increases user expectation for quick, synthesized results and introduces greater use of other media to the search process.
- Strategy Must Adapt to New SEO Reality: The rise of AI search, fueled by its convenience and worsening quality of traditional Google results (ads/spam), necessitates a dual-pronged optimization approach. Building strong domain and topical authority remains crucial, but new strategies must be implemented to ensure content is digestible by AI models.
AI Inside Google: AI Overviews, AI Mode
Inside Google, AI has been pushed in the form of summaries or AI Overviews (AIOs). These sometimes appear at the top of results, most frequently for highly informational and technical concepts such as science, medicine, and law. They provide AI-powered results that occasionally deviate from the highest-ranked content.
Google AI Overviews are a shift from ‘search engine’ to ‘answer engine’. In other words, Google is trying to answer every question a user has before they leave the search page. It has even been described as “doing the search for you.” This is also where the infamous ‘zero-click search’ comes from. A user doesn’t click on anything in a results page because the AI Overview already has the answers.
Example search showing where Google search AI mode is located. Source: google.com.
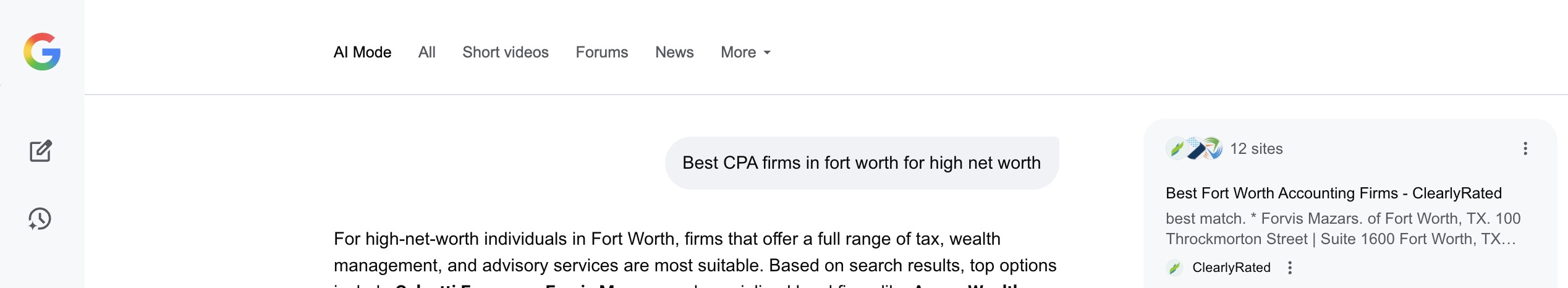
Example search showing Google AI Mode results. Note a sidebar providing site suggestions. Source: google.com.
AI Overviews aren’t the only Google-side strategy though. An AI tab—known as AI mode—now occupies the search engine’s leftmost position once held by ‘All’. The feature was announced March of this year and rolled out soon after. With AI Mode, Google hopes to hit further benchmarks. The company has been building a wide-ranging suite of AI products for some time, ranging from drafting emails to predicting the shape of organic molecules.
Interestingly, both AI features build on existing search results using what is known as query fan-out. A user prompts the AI, and it divides the search query into sub-queries, thus ‘fanning out’. For instance, AI Overview might split a search for “CPA firms near me” into nearest location, hours/availability, pricing and services offered. By aggregating several similar sub-results, the AI gets a detailed, multi-dimensional answer to one search query.
As a consequence of their speed and depth, these AI features are now overtaking the organic and paid results, making traffic zero-click and the financial model of informative content redundant.
Historically, sites like blogs made money with sidebar ads. Ad revenue went back to Google, incentivizing the quality of the search engine and rewarding the most informative content on a blog.
Now, users can simply read AI Overviews or ask in AI mode, so they never see visit pages and never see ads. This flips the economics of search on its head. AI is currently not monetized outside of subscription—which itself doesn’t cover the immense processing cost.
The problem is that now, there’s currently almost no financial incentive to produce content unless its an outreach/conversion channel.
AI Outside Google: LLM Chatbots, Specific Services
AI chatbots—also known as large language models—are beginning to divert certain kinds of search activity away from Google. While they produce different answers and rely on different data sources, they collectively offer a conversational alternative to Google’s results page.

Global AI search traffic vs. Google traffic over time. Source: wix.com/studio/ai-search-lab/research/ai-search-vs-google.
Despite this momentum, these tools are far from toppling Google’s dominance. Google still drives 300 times more traffic to websites than all AI platforms combined. That being said, the rise in AI-driven referrals has made AI chatbots an increasingly important area of interest for SEO.
Two AI chatbots stand out as top contenders in search: OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Perplexity. Among AI clicks to websites, ChatGPT comprises 77%, with Perplexity at a distant 15%. Both are AI models that can be asked questions on their respective websites or apps. But both work differently: ChatGPT primarily uses its training data to provide information while Perplexity generates results after grabbing relevant search results.
Beyond these general-purpose chatbots, an ecosystem of specialized ones have cropped up.
Cursor AI is an example of an AI-integrated coding environment. Then there are AI browsers which integrate models with real-time data like browsing history and currently open tabs. Meta has an AI suite named Llama which primarily targets smaller, simpler searches and seeks a more ‘everyday’ integration. All of these different use cases indicate that AI impacts search in many different areas in many different ways at once.
Impact on Search
These are the major AI products available that compete in search. So, what impact do they have on search?
For one, AI is increasing the multimodality of search. Users can submit not just images, but entire files or links to assist with a search query. AI tools can interpret charts, analyze screenshots, or summarize documents. As a result, strategies optimizing for various types of media have proven to drive referrals.
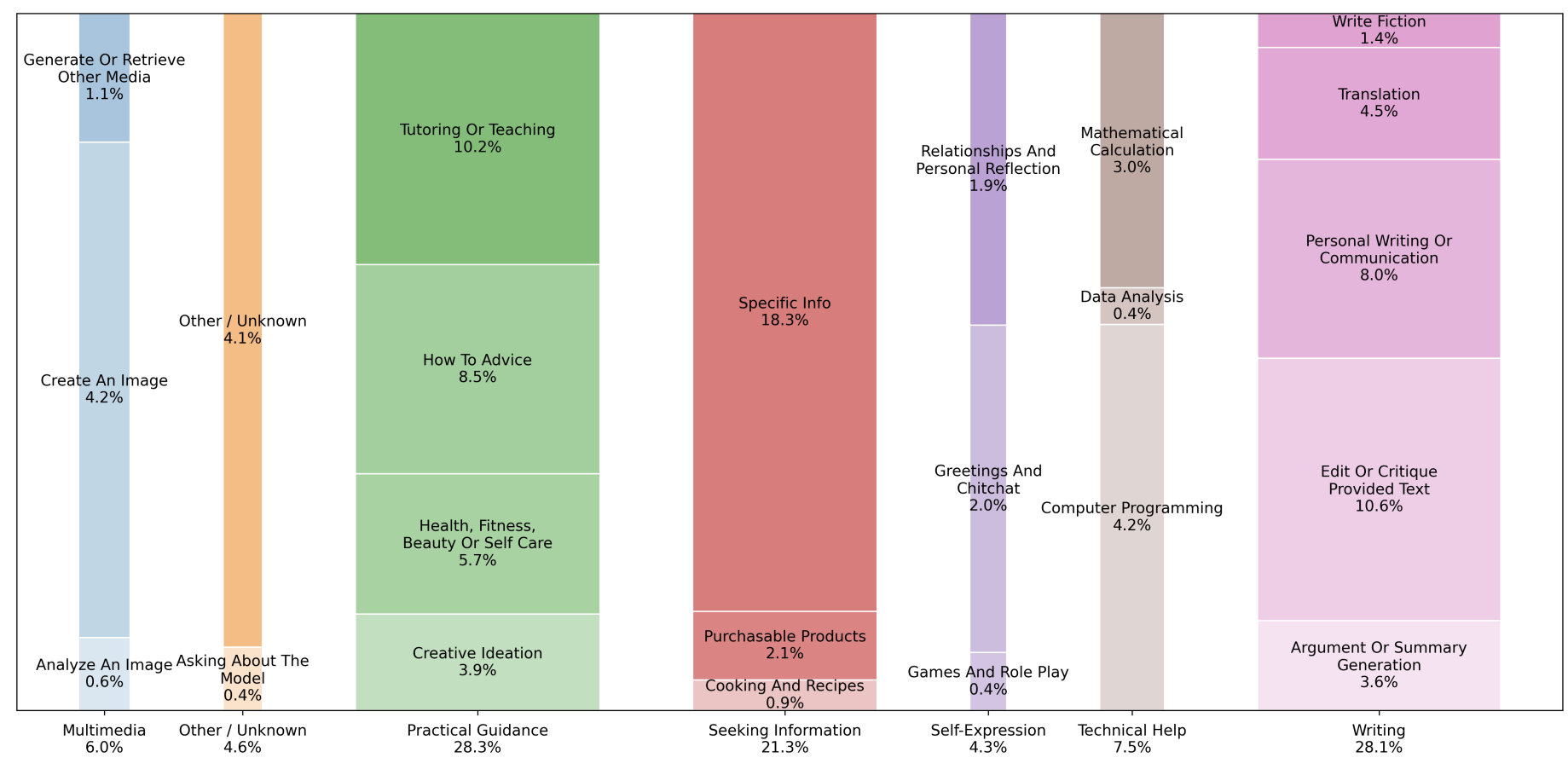
Breakdown of ChatGPT topic by percentage using 1.1 million sampled conversations. Source: How People Use ChatGPT, Chatterji et al. 2025.
The biggest element influencing traditional search is that AI is a ‘black box’ which provides information from training data without always leaving citations, a fact especially pronounced in ChatGPT. Adding that AIs also answer more thoroughly than search results, it’s understandable that the overall click-through rate on AI citations is abysmal.
Even further, AI prefers both long- and short-form content, leaving middle is hollowed out. On one hand, content is more likely to get cited the more concise it is. AI loves concise content, and it is naturally short. On the other hand, authoritative content performs well for complex queries and those that need lots of facts. Truly informative content for topics like health and science have much to say, so they are longer. AI also likes to cite entire journals or articles.
While the traffic impact of AI remains small, AI platforms make users to increasingly expect generated answers over lists of search results. They rank information and save time on the same search inputs as in Google. Instead of combing blogs to find and put together information, a chatbot simply delivers the result.
AI is not yet fully displacing Google, but it is reshaping expectations and changing which types of content is presented to users. Its growing place in search shows that visibility depends more and more on following their directive to provide quick, clear answers backed by relevant facts and data.
In other words, SEO needs to adapt to a conversation-oriented world different to that of Google.
Why People Might Prefer AI Over Regular Search
Understanding the growing influence of AI in search requires examining what draws users to it over something like Google. There are two competing factors at play that drive this shift.
Lower Attention Span: The first is a problem of attention. Attention spans are much shorter today than ever before. The rise of social media and, more recently, of short-form videos has lead to a pronounced desire for quick gratification.
People spend an average of over 2 hours per day on social media in 2025. AI provides a fast response and cuts time spent searching and thinking, so people are naturally attracted to this alternative. Consequently, a reduced mental load leads to a rise in adoption.
Worse yet, AI search also decreases cognitive capacity as it fills the mental difficulty of manual, traditional search. People lose the capacity to think by outsourcing that capacity and subsequently become reliant on AI models to think for them. The more AI handles, the less users practice the handling themselves.
Worsening Google Results: It’s clear where AI search’s rise comes from. However, there’s a second problem that Google suffers right now: quality decline. AI makes search easier at the same time that using Google becomes harder.
Results pages are now seeing a problem with AI’s ease of use: uninformative or spammy content. This type of content at best reorganizes already existing information, and at worst hurts user experience. Despite Google’s attempts to quell what it deems “scaled content abuse,” rankings continue to see impact from the shotgun approach that AI has enabled.
PPC is another part of the problem that Google is responsible for. Yet, it continues to draw users away from the search engine. Users of Google are frustrated with how many ads appear—and how seamlessly they integrate—when seeking organic results instead. It’s party understandable from Google’s perspective, as cost-per-click keeps increasing year over year.
In short, the rise of AI search can be attributed to shrinking attention spans and an increase in ads and content quantity on Google. Traditional search feels like a slog and often produces worse results than AI as the transition to AI keeps accelerating further.
What This Means For Businesses
While all of this paints a picture of what’s going on, it doesn’t explain what businesses can do about it. Overall, there are two important takeaways.
First: optimize, optimize, optimize. Do it for AI or do it for Google, as either will help websites weather the change. We made a comprehensive guide on how to make websites readable for AI.
There are many ways to optimize. Everything from the structure of a website down to the tags the website’s code uses are all signals that help AI digest content and know its informational worth. These steps and general SEO are the best ways to handle the upended search landscape.
Among general SEO steps, building authority is the most important one. Authority was already historically important, and now it’s more important as Google ranking shake-ups “become ‘the new normal'”. Authority is traditionally split into domain authority and topical authority, and both contribute to rankings.
Domain authority refers to the perceived standing of a website by search engines and AI, and topical authority refers to how well a search topic is covered by a website’s content. Plenty of guides already exist on how to build authority. Strategies like pillar pages, quality backlinks, and consistent brand signals all contribute to it.
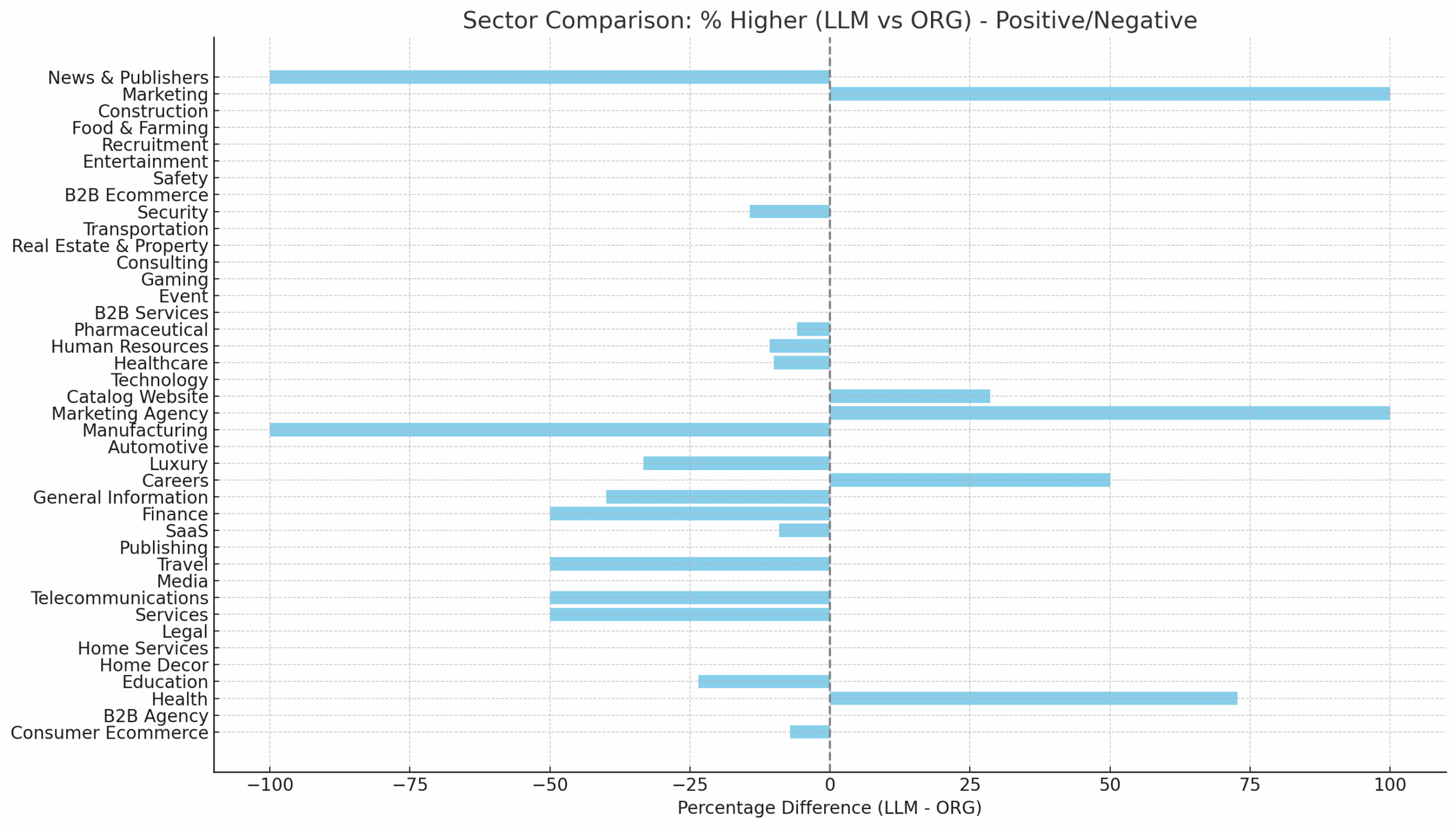
AI-based search intent difference from organic varies widely by site topic. Source: salt.agency.
Second, even with the increase in AI referrals, it might not be the best thing to pursue. While Google and Bing claim that AI traffic is higher quality, a study found a nuanced picture. In some websites the AI traffic performed better, in other the organic. The above chart is a good way to determine if AI-first optimization is a good priority.
What trends really indicate is a splitting of SEO: one layer of search engine optimization, one layer of AI optimization. A new medium means new opportunity to connect with potential customers.
However, it’s important to enter this new medium carefully; what matters is the individual context of the website and its priorities. Optimizing for AI growth will always have some impact, but the traffic it generates could be less important than simply optimizing for Google search results. Even then, optimizations should impact both.
The brands winning the next phase of search are the ones treating AI as a second front and continue to build authority and good UX.
There has been a lot of hype surrounding AI. While it does provide significant opportunity, jumping into a new technology without caution nor proven strategy is unlikely to yield good results. AI optimization is not a replacement for Google optimization, but rather a parallel channel to understand and work toward.
Contact Us
It’s always important to be on top of changes in search as they happen. Have questions about how evolving AI search will impact your business? Contact our team of SEO experts at Flashpoint Marketing so you can stay competitive and ready for whatever comes next.

