SEO Guides, Tips & More!
Learn from Our Experience
An Introduction to Google Search Console
In Summary
- Google Search Console: Search Console offers website managers technical status updates, insights into Google’s view of pages, and advice for fixing errors and improving functionality. Unlike Google Analytics, Search Console provides the data needed to proactively manage site improvements, enhance search rankings, and assess content indexing.
- Key Features and Reports for Deeper Analysis: The platform provides essential tools like URL Inspection and a mobile-friendly test, alongside detailed reports. Reports such as performance (for clicks and queries), coverage (for indexing status), and Core Web Vitals (for user experience) offer data beyond what Google Analytics can provide alone.
- Actionable Steps to Improve Site Traffic and Speed: Utilize the performance report’s data on user queries, clicks, and impressions to inform content strategy and create new, relevant material. Furthermore, the HTML Improvements section helps identify and fix issues like duplicate or missing title tags, directly contributing to better page loading speed and overall SEO health.
SEO and website maintenance never stop. They’re part of a continual process of monitoring, adjusting, and improving website performance. The majority of organic and paid search traffic comes from Google, so it makes sense to direct limited time and resources into optimizing sites for the Google platform. When all the pages on a website are already optimized with SEO keywords, metadata, and page titles, it can be hard to know what else to do to improve site performance. What if there was a way to get feedback directly from Google? There is, and marketers may not be aware of it.
With Google Search Console, website managers have access to more analytics, data, and feedback than Google Analytics can provide on its own. It gives site managers insight into Search rankings, SEO data, helps sites rank better on Google, and even gives advice on how to fix errors or improve functionality. While Google Analytics does provide real-time access to who’s visiting a site, it’s a more of a reactive tool to measure site performance. Google Search Console helps marketers proactively manage their sites and see which parts need work to get better results in search rankings.
Why Use Google Search Console?

Yes, it’s one more tool and one more account to monitor. And we know that accounting marketers are already wearing a lot of hats. That’s why making the most of limited time with better resources is so important. It doesn’t cost anything to sign up for a Search Console account, it integrates with Analytics, and registering the site with Search Console only takes a few steps.
Beyond tracking site performance in Google search rankings, marketers can also:
- Receive technical status updates about their site
- See how Google views different pages
- Get tips on how to improve Google’s crawling
- Check mobile usability
- Track content marketing efforts
- Communicate with Google on penalties, errors, or other comments
Although Analytics does give information about which keywords people use to find the website, Search Console tells marketers whether Google perceives the content in the same way. Content Keywords display the most commonly indexed keywords on the website, which allows marketers to assess whether a certain tactic or keyword is working. Search Console can break this data into desktop and mobile versions so marketers know how the viewing experience might be affecting search traffic and click-through-rates.
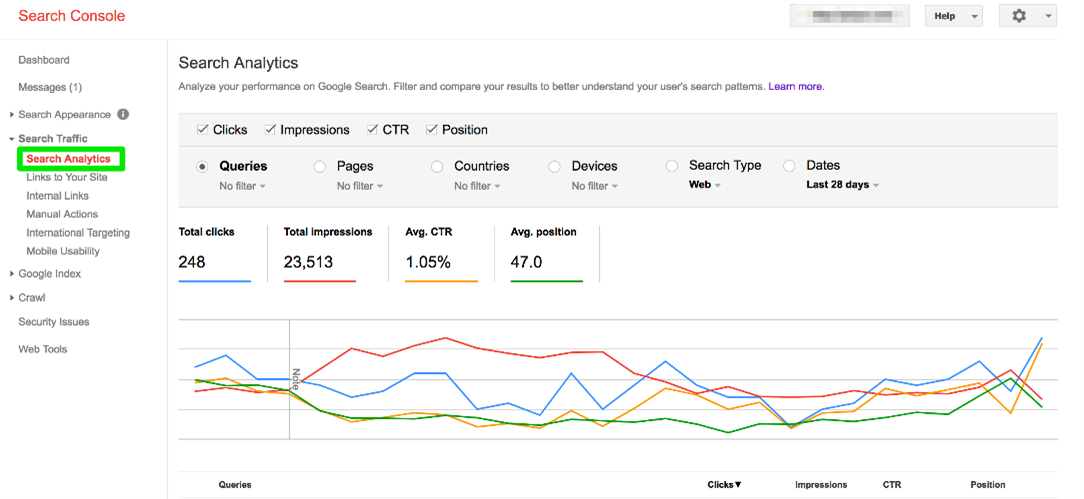
Image courtesy of Search Engine Journal.
It’s also easy to see how often a site appears in Google search results and which pages and queries earn the best click-through rate. Especially when adding new pages to a site, or launching a redesign of an existing site, Search Console puts marketers in charge of making sure their site index is being crawled. Conversely, marketers can also use Search Console to remove old pages that shouldn’t be crawled anymore. It can also be used to keep a site clean and free of spam and other indexing errors.
And, when Search Console is added to Analytics, there is no separate page or sign-in to access the data – it’s all viewable under the main Analytics platform. Examples of how the two tools differ are below.
Google Analytics | Google Search Console |
| Total # of user queries across the web | Most significant keywords from Google |
| Info on site visitor conversions | Info on why the conversions happen |
Search Console provides a more robust data experience than Analytics on its own. When paired together, they are a comprehensive data analytics and content performance tool for websites.
Features of Google Search Console
The current Search Console contains several reports and features, outlined below. There are also several other legacy reports and tools that are still available, such as crawl stats, URL parameters, data highlighter tool, and more.
Features
- Overview Page – The Overview Page is a summary of the website’s performance and any actions or security issues. There are also graphs of total clicks, errors, and suggested enhancements for the site. Security issues can be used to fix the site using Search Console’s troubleshooting tips.
Tools
- URL Inspection – Marketers can either test the URL of a live page or see what information Google has about a specific page. The data will include HTML code and errors, mobile usability errors and code, JavaScript output and issues that arise when Google renders a page, and more. This tool can be used to troubleshoot crawling errors on a site or to fix and retest a page before submitting it to Google for indexing.
- AMP Test – AMP pages, or Accelerated Mobile Pages, are essentially open-source HTML pages that are optimized for mobile. This tool tests AMP pages for validity. It is a bit technical and best used by SEO experts and developers.
- Mobile-Friendly Test – Tests whether a certain page is mobile-friendly.
- Change of Address – Used when a site is migrated to a different domain.
- Removals – Marketers can use this tool to temporarily block URLs on the site from appearing in Google search results, or to clear the search snippet until the next document crawl. This tool will also show a history of block requests.
Reports
- Performance Report for Search and Discover – This report tells how many people saw and clicked on the site in Google search, what search queries resulted in showing the site, and average search position. Data includes clicks, impressions, click-through-rate, and position, plus query strings that users used to get to the site. The data can be grouped by page URL, country, or device.
- Coverage Report – Shows how each page on the site is indexed. Pages that cannot be indexed include a description as to why.
- Sitemaps Report – Displays which sitemaps have been submitted, statistics, and any errors in processing the sitemaps. This report is useful if marketers want to debug their site or if Google can’t seem to find certain pages.
- Core Web Vitals Report – Demonstrates real-world usage of page performance. Check this report to see how pages look for visitors and fix poorly performing pages.
- Mobile Usability Report – See how all pages on the site perform on a mobile device. This report can also be used to fix mobile usability issues as they arise.
- AMP Report – Marketers can see which AMP pages are or are not indexed.
- Rich Result Status Reports – Rich results are Google search results with an image; rich snippets are a thumbnail image with text, and rich cards are a larger image with a linking title. This report lets marketers see which rich results Google could or could not crawl. This report is helpful for SEO experts and site developers as it’s a bit more complicated and in-depth than others.
- Manual Actions Report – Displays any manual actions against a site, which happen when users report an issue to Google that doesn’t meet Webmaster guidelines. An example would be a page trying to manipulate the search index.
- Security Issues Report – Displays any security issues on a site, such as browser alerts for dangerous or hacked content.
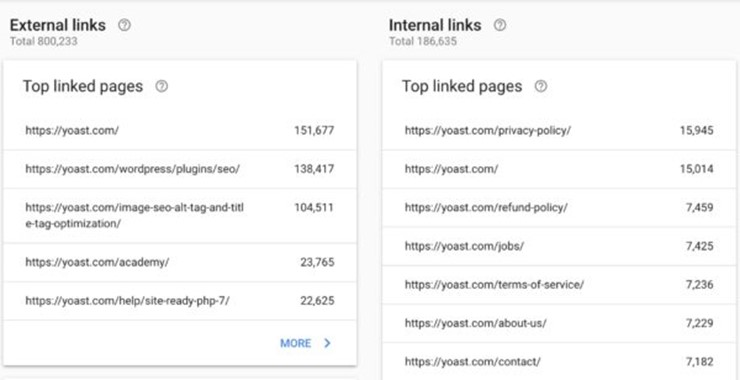
- Links Report – Shows marketers which sites link to theirs, what the link text is, and internal link targets within the site itself. This can be used to determine whether third-party links are spammy or legitimate.
Using Search Console to Improve a Website
All the features in the world won’t matter if they can’t be easily used. These are just a few tips based on our experience that will be helpful for beginner to intermediate Search Console users who want to make the most out of their time with the tool.
To improve content marketing efforts, navigate to “Search Analytics” under Search Traffic. Select clicks, impressions, CTR, and position as the benchmarking data. Start using these analytics to determine what drives traffic the site; Queries are a good place to start.
This will open up a view into which queries are driving web traffic. The following report will not only produce actual keywords, it will also display the number of clicks from each query, impressions, CTR, and position in Google search results. Very valuable data.
Our tip is to use this information to cross-check existing content on the site and create new content based on what people are searching for.
Another way to use Search Console is to improve page loading speed. This is done through fixing things like large images, heavy page elements, and HTML coding issues. With Search Console, marketers can improve their site’s HTML issues by going to “HTML Improvements” under Search Appearance. The result is a list of every HTML issue affecting the site.
Look for things like duplicate title tags and meta descriptions, title tags that either too short or too long, missing title tags, and more. A table can be downloaded for easy reference.
Google Search Console can also be used to submit the latest blog post to Google’s crawling index, analyze clickable elements of mobile pages, improve the CTR of rich content, and more.
Getting Started with Google Search Console
Accounting marketers that don’t yet have a Google Search Console account and aren’t sure where to start can click here. There are four different tracks to choose based on which level best describes the level of experience and time commitment to maintaining and managing a website. Google also has a great video series for beginner users, or marketers that just want to brush up on the tools and features.
Flashpoint Marketing can help set up Search Console, conduct training on how to use and apply the reports and tools, and help accounting marketers monitor their website’s performance. Contact us to find out how it works.

